There is a persistent story we tell ourselves about quantum mechanics:* that it reveals reality to be fundamentally strange, paradoxical, or hostile to common sense. Particles in two places at once. Cats be both alive and dead. Worlds multiplying to save appearances.
I’ve never found that story convincing.
What I do find convincing is a simpler diagnosis: that we are applying a cognitive tool far beyond the conditions under which it earned its authority – and then mistaking the resulting discomfort for metaphysical insight.
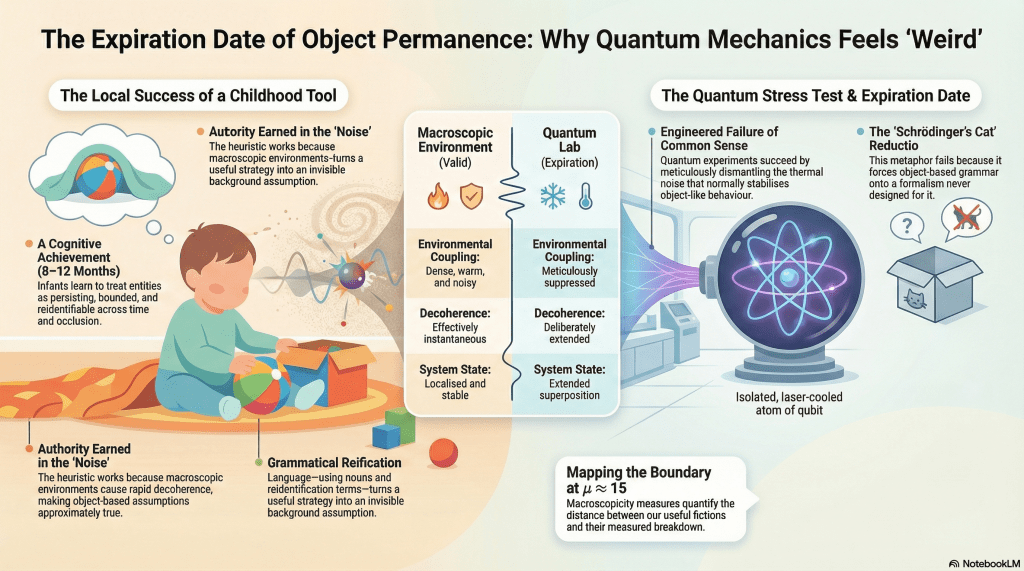
Object permanence is one of our earliest and most successful heuristics. It allows infants to track toys behind sofas, caregivers behind doors, and threats behind occlusion. Without it, coordinated action would be impossible. With it, the world becomes navigable, predictable, and stable. It is a genuine cognitive achievement. But it is not a universal guarantee about reality.
In a new essay, The Expiration Date of Object Permanence: Heuristics, Grammar, and Quantum Pseudoproblems, I argue that much of what we call ‘quantum weirdness’ arises from the uncritical extension of this heuristic into domains where its ecological licensing no longer holds. The problem is not that quantum mechanics violates common sense. The problem is that we quietly treat common sense as metaphysics.
Quantum mechanics functions here not as a mystery generator, but as a stress test. Recent matter-wave interference experiments with increasingly massive systems show that object-based expectations fail quantifiably under carefully engineered conditions. When environmental coupling is suppressed, when decoherence is delayed, when the world is no longer warm, noisy, and forgiving, the assumptions underwriting object permanence simply stop paying rent.
Nothing spooky happens. A heuristic expires.
The essay also takes a dim view of some familiar cultural furniture. Schrödinger’s cat, for example, was introduced as a reductio – an intentionally absurd demonstration of what happens when microscopic formalism is naively scaled up. That it now circulates as an explanatory image tells us less about quantum mechanics than about the tenacity of object-grammar. Even jokes cannot escape it.
Interpretations fare no better. I suggest that the appeal of frameworks like Many-Worlds is not exhausted by their technical merits. They also function as strategies for preserving object-based reidentification – ways of ensuring that there is still something that can be pointed to, counted, and followed through time, even if the price is ontological inflation.
None of this denies the reality of quantum phenomena, nor does it pretend to solve the measurement problem. The essay is deliberately deflationary. Its claim is methodological, not revisionary: that many of the puzzles we inherit are artefacts of treating developmentally acquired heuristics as if they were unconditional features of the world.
Philosophy’s task, on this view, is not to make reality intuitive. It is to recognise when intuition has reached the end of its jurisdiction.
The paper is now available on Zenodo and will be indexed shortly on PhilPapers. As always, comments, objections, and principled misreadings are welcome.
This post and the underlying essay were inspired by a Nature article: Probing quantum mechanics with nanoparticle matter-wave interferometry, published on 21 January 2026. I get annoyed watching people misunderstand quantum mechanics and its effects, so I decided to address some of the issues in an essay. Read this essay as well as mine, which will explain why the paradoxes and ‘spooky behaviour’ of QM are only counter-intuitive if you’ve fallen into this heuristic trap.