I’ve been reading Bernard Williams lately, and I’ve written about his work on Truth and Truthfulness. I’m in the process of writing more on the challenges of ontological moral positionsand moral luck. I don’t necessarily want to make contemporary news my focal point, but this is a perfect case study for it. I’ll be releasing a neutral philosophy paper on the underlying causes, but I want to comment on this whilst it’s still in the news cycle.
The form of xenophobia is a phenomenon occurring in the United States, though the ontological split is applicable more generally. For those unfamiliar with US news, I’ll set this up. The United States is currently deploying federal enforcement power in ways that deliberately bypass local consent, blur policing and military roles, and rely on fear as a stabilising mechanism. Historical analogies are unavoidable, but not required for the argument that follows. These forces have been deployed in cities that did not and do not support the Trump administration, so they are exacting revenge and trying to foment fear and unrest. This case is an inevitable conclusion to these policy measures.
tl;dr: The Law™ presents itself as fact-driven, but only by treating metaphysical imputations about inner life as if they were empirical findings. This is not a flaw in this case; it is how the system functions at all.
NB: Some of this requires having read Williams or having a familiarity with certain concepts. Apologies in advance, but use Google or a GPT to fill in the details.
Why the Minneapolis ICE Shooting Exposes the Limits of Bernard Williams
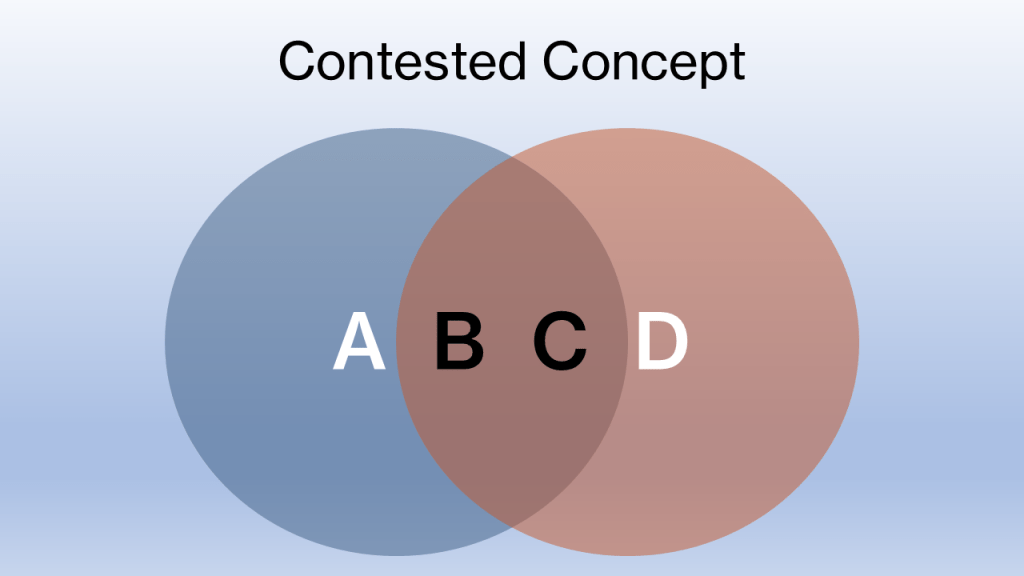
The Minneapolis ICE shooting is not interesting because it is unusual. It is interesting because it is painfully ordinary. A person is dead. An officer fired shots. A vehicle was involved. Video exists. Statements were issued. Protests followed. No one seriously disputes these elements. They sit in the shared centre of the Venn diagram, inert and unhelpful. Where everything fractures is precisely where the law insists clarity must be found: intent and motive. And this is where things stop being factual and start being metaphysical.
The Comfortable Fiction of Legal Facts
The legal system likes to tell a comforting story about itself. It claims to be empirical, sober, and evidence-driven. Facts in, verdicts out. This is nonsense.
What the law actually does is this:
- It gathers uncontested physical facts.
- It then demands a psychological supplement.
- It treats that supplement as if it were itself a fact.
Intent and motive are not observed. They are inferred. Worse, they are imposed. They are not discovered in the world but assigned to agents to make outcomes legible.
In Minneapolis, the uncontested facts are thin but stable:
- A U.S. Immigration and Customs Enforcement (ICE) agent, identified as Jonathan Ross, shot and killed Renée Nicole Good in Minneapolis on 7 January 2026.
- The incident involved Good’s vehicle, which was present and moving at the time shots were fired.
- Ross fired his weapon multiple times, and Good died from those gunshot wounds.
- The Department of Homeland Security (DHS) claims the agent acted in self-defence.
- Video footage exists that shows at least part of the encounter.
- The case ignited protests, widespread condemnation from local officials, and political pushback.
This creates a shared intersection: vehicle, Ross, shots, and that ‘something happened’ that neither side is denying.
The Law smuggles metaphysics into evidence and calls it psychology.
None of these facts contain intent. None of them specify motive. They do not tell us whether the movement of the vehicle was aggression, panic, confusion, or escape. They do not tell us whether the shooting was fear, anger, habit, or protocol execution. Yet the law cannot proceed without choosing.
So it does what it always does. It smuggles metaphysics into evidence and calls it psychology.
Intent and Motive as Institutional Impositions
Intent is treated as a condition of responsibility. Motive is treated as its explanation. Neither is a fact in anything like the ordinary sense. Even self-report does not rescue them. Admission is strategically irrational. Silence is rewarded. Reframing is incentivised. And even sincerity would not help, because human beings do not have transparent access to their own causal architecture. They have narratives, rehearsed and revised after the fact. So the law imputes. It tells the story the agent cannot safely tell, and then punishes or absolves them on the basis of that story. This is not a bug. It is the operating system.
Where Bernard Williams Comes In
This is where Bernard Williams becomes relevant, and where his account quietly fails. In Truth and Truthfulness, Williams famously rejects the Enlightenment fantasy of capital-T Truth as a clean, context-free moral anchor. He replaces it with virtues like sincerity and accuracy, grounded in lived practices rather than metaphysical absolutes. So far, so good.
Williams is right that moral life does not float above history, psychology, or culture. He is right to attack moral systems that pretend agents consult universal rules before acting. He is right to emphasise thick concepts, situated reasons, and practical identities. But he leaves something standing that cannot survive the Minneapolis test.
The Residue Williams Keeps
Williams still needs agency to be intelligible. He still needs actions to be recognisably owned. He still assumes that reasons, however messy, are at least retrospectively available to anchor responsibility. This is where the residue collapses.
In cases like Minneapolis:
- Intent is legally required but epistemically unavailable.
- Motive is legally explanatory but metaphysically speculative.
- Admission is disincentivised.
- Narrative is imposed under institutional pressure.
At that point, sincerity and accuracy are no longer virtues an agent can meaningfully exercise. They are properties of the story selected by the system. Williams rejects metaphysical Truth while retaining a metaphysical agent robust enough to carry responsibility. The problem is that law does not merely appeal to intelligibility; it manufactures it under constraint.
Moral Luck Isn’t Enough
Williams’ concept of moral luck gestures toward contingency, but it still presumes a stable agent who could, in principle, have acted otherwise and whose reasons are meaningfully theirs. But once intent and motive are understood as institutional fabrications rather than inner facts, ‘could have done otherwise’ becomes a ceremonial phrase. Responsibility is no longer uncovered; it is allocated. The tragedy is not that we fail to know the truth. The tragedy is that the system requires a truth that cannot exist.
Facts Versus Stories
The law does not discover which story is true. It selects which story is actionable.
The Minneapolis case shows the fault line clearly:
- Facts: bodies, movements, weapons, recordings.
- Stories: fear versus anger, defence versus aggression.
- The first is uncontested. The second does all the work.
And those stories are not epistemic conclusions. They are metaphysical commitments enforced by law. Williams wanted to rescue ethics from abstraction. What he could not accept is that, once abstraction is removed, responsibility does not become more human. It becomes procedural.
The Uncomfortable Conclusion
The law does not operate on truth. It operates on enforceable interpretations of behaviour. Intent and motive are not facts. They are tools. Williams saw that capital-T Truth had to go. What he did not see, or perhaps did not want to see, is that the smaller, more humane residue he preserved cannot bear the weight the legal system places on it.
Once you see this, the obsession with ‘what really happened’ looks almost childish. The facts are already known. What is being fought over is which metaphysical fiction the system will enforce.
That decision is not epistemic. It is political. And it is violent.