I’ve been working on A Language Insufficiency Hypothesis since 2018. At least, that’s the polite, CV-friendly version. The truer account is that it’s been quietly fermenting since the late 1970s, back when I was still trapped in primary school and being instructed on how the world supposedly worked.
Social Studies. Civics. Law. The whole civic catechism. I remember being taught about reasonable persons and trial by a jury of one’s peers, and I remember how insistently these were presented as fair solutions. Fairness was not argued for. It was asserted, with the weary confidence of people who think repetition counts as justification.
I didn’t buy it. I still don’t. The difference now is that I have a hypothesis with some explanatory power instead of a vague sense that the adults were bluffing.
I’ve always been an outsider. Eccentric, aloof, l’étranger if we’re feeling theatrical. It never particularly troubled me. Outsiders are often tolerated, provided they remain decorative and non-contagious. Eye rolls were exchanged on both sides. No harm done.
But that outsider position had consequences. It led me, even then, to ask an awkward question: Which peers? Not because I thought I was superior, but because I was plainly apart. How exactly was I meant to be judged by my peers when no one else occupied anything like my perspective?
Later, when I encountered the concept of fundamental attribution bias, it felt less like a revelation and more like confirmation. A peer-based system assumes not just similarity of circumstance, but similarity of interpretation. That assumption was dead on arrival.
Then there were reasonable persons. I was assured they existed. I was assured judges were trained to embody them. I had never met one. Even as a teenager, I found the idea faintly comical. Judges, I was told, were neutral, apolitical, and dispassionate. Writing this now from the United States, one hardly needs to belabour the point. But this wasn’t prescience. It was intuition. The smell test failed decades ago.
Before LIH had a name, I called these things weasel words. I still do, as a kind of shorthand. Terms like fair, reasonable, accountable, appropriate. Squishy concepts that do serious institutional work whilst remaining conveniently undefinable. Whether one wants to label them Contestables or Fluids is less important than recognising the space they occupy.
That space sits between Invariables, things you can point to without dispute, and Ineffables, where language more or less gives up. Communication isn’t binary. It isn’t ‘works’ or ‘doesn’t’. It’s a gradient. A continuous curve from near-certainty to near-failure.
Most communication models quietly assume a shared ontology. If misunderstanding occurs, the remedy is more explanation, more context, more education. What never sat right with me, even as a child, was that this only works when the disagreement is superficial. The breaking point is ontological.
If one person believes a term means {A, B, C} and another believes it means {B, C, D}, the overlap creates a dangerous illusion of agreement. The disagreement hides in the margins. A and D don’t merely differ. They are often irreconcilable.
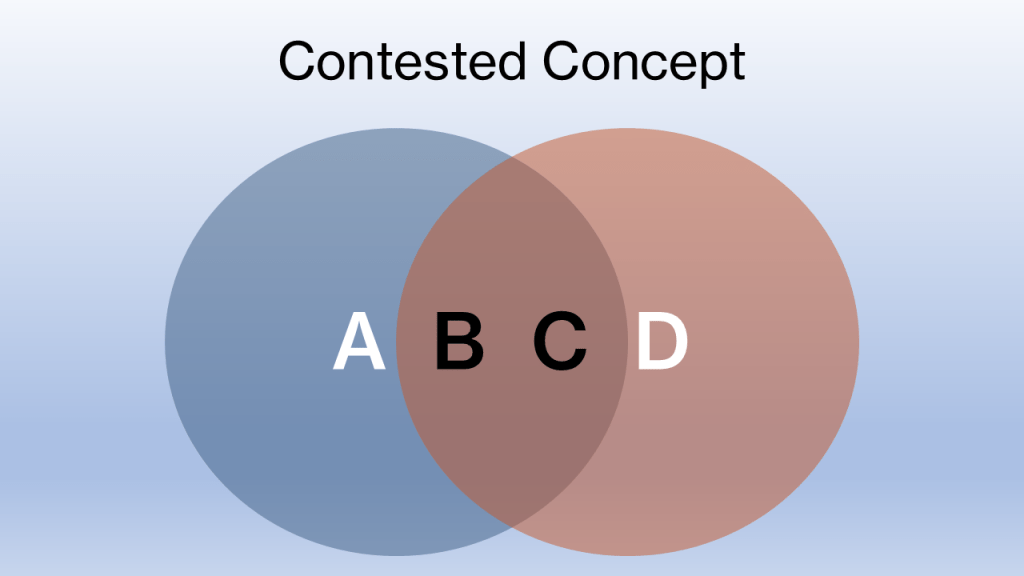
Note: This is illustrative and not to scale
Fairness is a reliable example. One person believes fairness demands punishment, including retributive measures. Another believes fairness permits restoration but rejects retribution, citing circumstance, history, or harm minimisation. Both invoke fairness sincerely. The shared language conceals the conflict.
When such disputes reach court, they are not resolved by semantic reconciliation. They are resolved by authority. Power steps in where meaning cannot. This is just one illustration. There are many.
I thought it worth sharing how LIH came about, if only to dispel the notion that it’s a fashionable response to contemporary politics. It isn’t. It’s the slow crystallisation of a long-standing intuition: that many of our most cherished concepts don’t fail because we misuse them, but because they were never capable of doing the work we assigned to them.
More to come.





