Jason from Philosopher Muse suggested a connexion between Transductive Subjectivity and the work of Stephen Batchelor. I wasn’t familiar with Batchelor, so — as one does these days — I asked a GPT to give me the lay of the land. The machine obliged, and the result was interesting enough that it warranted a post of its own. This is it.
The risk I take is that the GPT gets it wrong. If so, call me out.
Before anyone lights incense: I’m not suddenly a convert. Batchelor’s work and mine merely pass each other on adjacent footpaths. But the overlap is conceptually neat, and the divergence is even more telling.
Stephen Batchelor vs Transductive Subjectivity: A Brief Comparative Note
1. Shared Territory: The Self as Verb, Not Noun
Both Batchelor and Transductive Subjectivity reject the folk notion of a single, continuous metaphysical self.
- Batchelor (Secular Buddhism):
The self is an unfolding activity — impermanent, conditional, and without a stable essence. His “not-self” is a practice of disidentification from the imagined nugget of continuity we cling to. - Transductive Subjectivity:
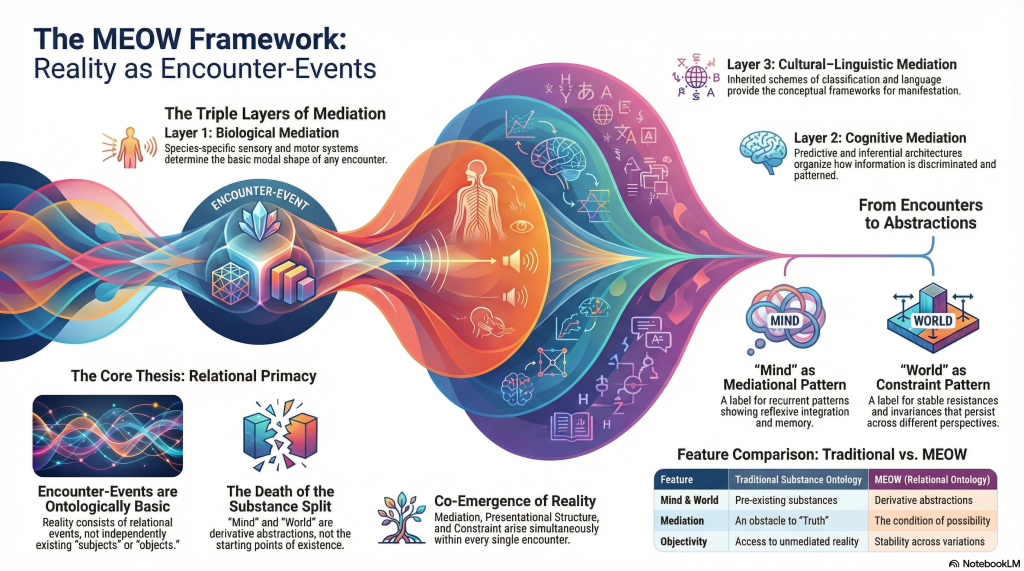
The self is a finite series: S₀ → S₁ → S₂ → … → Sₙ, each produced through the pressure of relational structures (R). Identity is what results when the world meets the organism. Nothing metaphysical required; just biology, cognition, language, and institutions doing their thing.
Overlap: Both positions dismantle the enduring pearl-of-self. Both frame identity as something generated, not possessed.
2. Divergent Aims: Inner Liberation vs Structural Clarity
This is where the paths fork.
- Batchelor’s Agenda:
Primarily ethical and therapeutic. The point of denying a fixed self is to reduce suffering, ease attachment, and cultivate a more responsive way of being. - TS’s Agenda:
Metaphysical accuracy in the service of ethical clarity. If the self is a serial construction rather than a diachronic monolith, then retributive justice collapses under its own fictions. No self, no desert. No desert, no justification for revenge-based punishment.
Batchelor wants flourishing. I want rigour. Accidental cousins.
3. Methodological Differences: Distillation vs Reconstruction
Batchelor performs what you might call Buddhism sans metaphysics.
A very Western manoeuvre:
- keep impermanence
- keep ethical insight
- jettison karma, rebirth, cosmology
- rebrand the remnants as a secular spiritual practice
Practitioners dislike this because he amputates the structural scaffolding that supported the doctrine.
TS, by contrast, doesn’t distil anything. It reconstructs selfhood from first principles:
- No causa sui
- Episodic, indexical selfhood (Strawson)
- R→S transduction (MEOW)
- No diachronic essence
- No metaphysical ballast
If Buddhism aligns with TS, it’s incidental — the way two different mathematicians can discover the same function by entirely different routes.
4. Conceptual Architecture: Dependent Origination vs MEOW’s Tiers
- Batchelor:
leans on dependent origination as a philosophical metaphor — phenomena arise through conditions. - TS:
models the exact channels of that conditioning via MEOW:
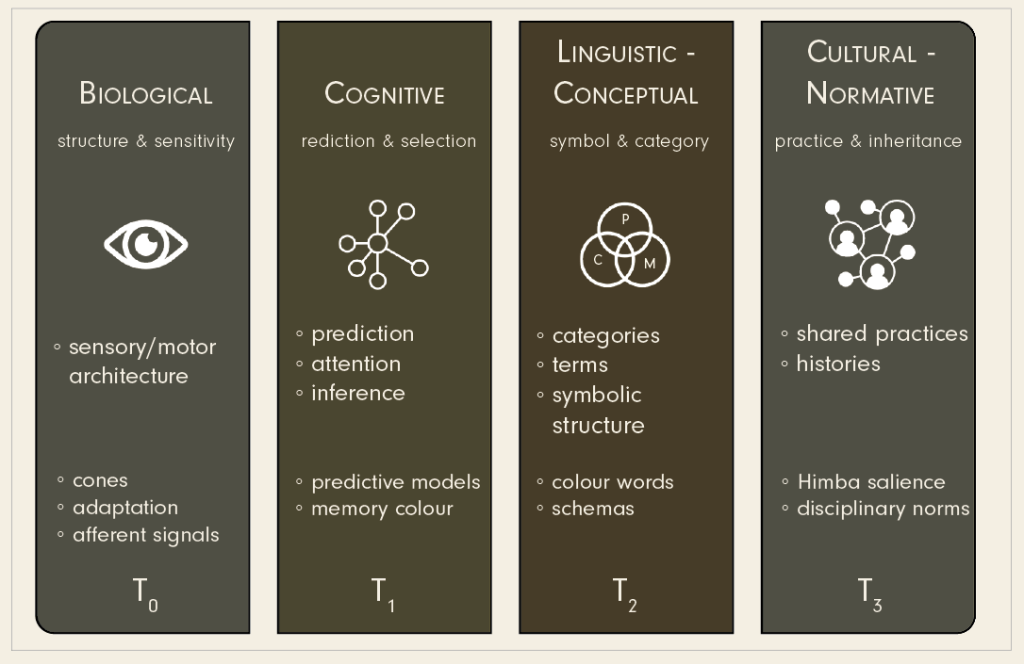
T0 → biological signals
T1 → cognitive architecture
T2 → linguistic formats
T3 → social-technical pressures
Where Batchelor says “everything is contingent,” TS says “yes, and here is the actual machinery.”
5. Different Stakes
- Batchelor: freeing the person from clinging to an imaginary core.
- TS: freeing ethics, law, and social design from pretending that metaphysical core exists.
One is therapeutic; the other is diagnostic.
A Key Point of Departure: Batchelor Works with Folk Psychology; TS Rejects Its Premises
There is one more divergence worth highlighting because it cuts to the bone of the comparison.
Batchelor accepts the phenomenological feel of the continuous self as a legitimate starting point. His work is therapeutic: he begins where the person is, in the lived experience of being “me,” and then encourages a gentle loosening of the grip on that intuition.
Transductive Subjectivity takes a different route entirely.
For TS, the continuous, diachronic self isn’t a psychological obstacle to be softened — it is a category mistake. A narrative compression artefact. A heuristic with pragmatic uses, yes, but no metaphysical legitimacy. Batchelor tries to transform our relation to the folk-self; TS denies that the folk-self was ever more than a convenient fiction.
Batchelor says:
“You seem like a continuous self; now learn to hold that lightly.”
TS says:
“You seem like a continuous self because the system is glossing over discontinuities. The sensation itself is misleading.”
In other words:
- Batchelor redeems the experience.
- TS disassembles the model.
He treats the “self” as something to relate to differently.
TS treats the “self” as an ontological construct to be replaced with a more accurate one.
This is not a difference of ethical aim but of metaphysical foundation.
Batchelor trims the folk psychology; TS declines the invitation altogether.
Closing Note
So yes — the connexion Jason spotted is real. But it’s genealogical, not derivative. We arrive at similar conclusions for different reasons and with different consequences.
Batchelor is pruning a tradition.
Transductive Subjectivity is rebuilding the ontology.
And both, in their own way, make the continuity-self look like the rhetorical placeholder it always was.