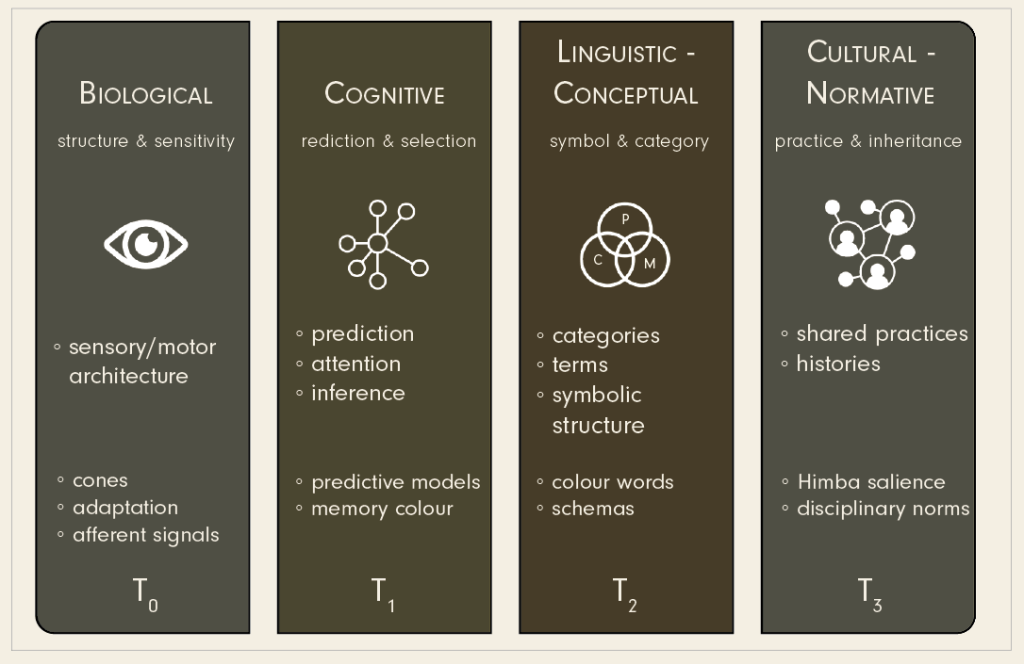
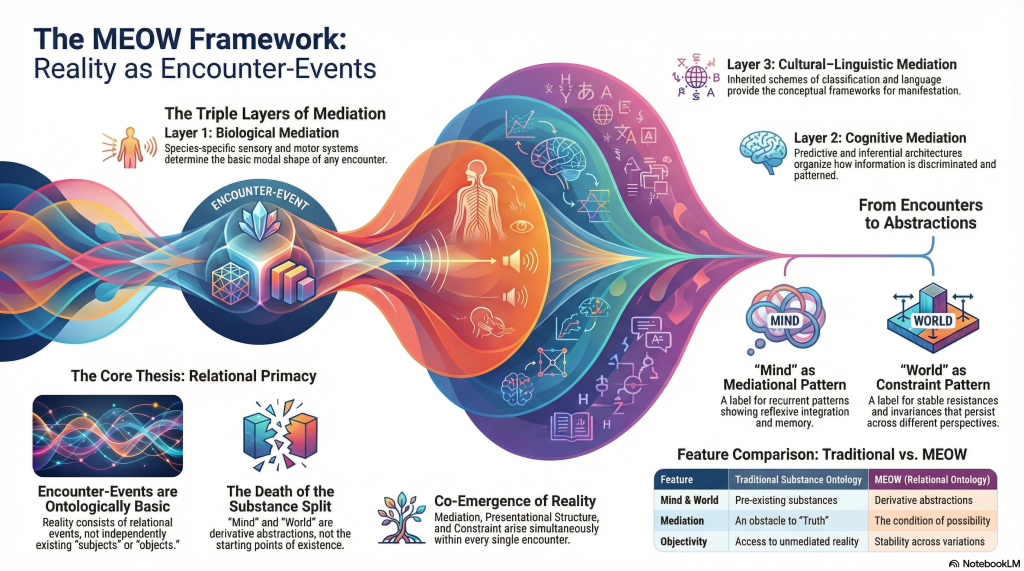
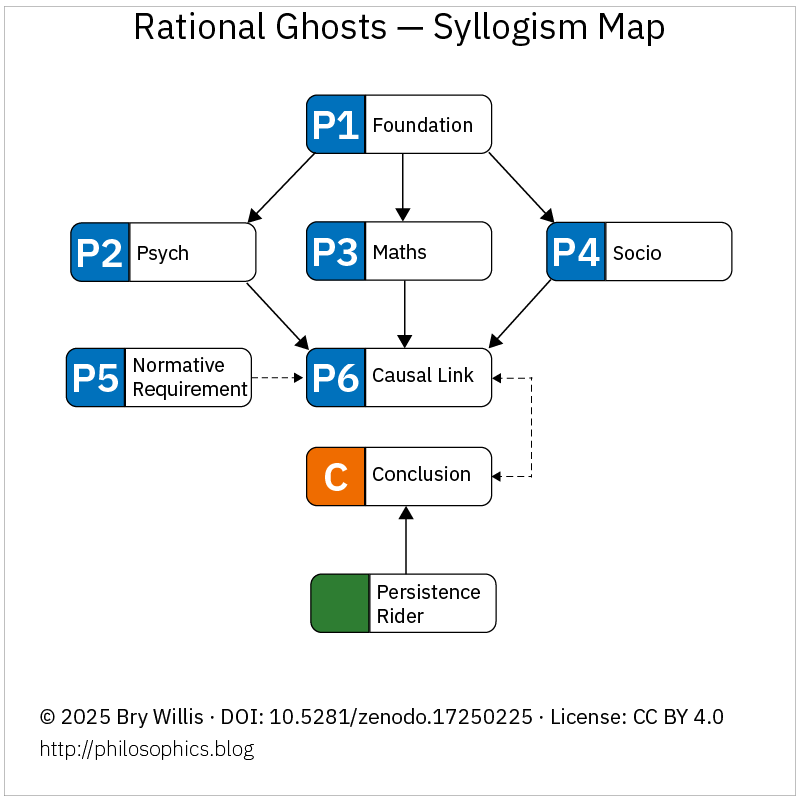
We tend to think of speed limits as facts. Numbers. Neutral. Posted. Enforced. And yet almost no one treats them that way.
Roads are engineered to handle speeds well above the numeral on the sign. Police officers routinely tolerate a band of deviation. We know they’ll allow around ten miles per hour over the stated limit. They know we know. We know that they know that we know. Ad infinitum.
Courts accept that instruments have margins of error. Drivers adjust instinctively for weather, traffic density, visibility, vehicle condition, and local customs. A straight, empty motorway at 3 a.m. is not experienced the same way as a narrow residential street at school pickup time, even if the number on the sign is identical. Everyone knows this. And yet we continue to talk about the speed limit as if it were an unmediated fact about the world.
This is not a complaint about traffic law. Speed limits work remarkably well, precisely because they are not what they appear to be. They are not discoveries about nature, but stabilised conventions: administrative thresholds designed to coordinate behaviour under uncertainty. The familiar numbers – 30, 50, 70 – are not found in the asphalt. Never 57 or 63. They are chosen, rounded, and maintained because they are legible, enforceable, and socially negotiable. What makes speed limits interesting is not their arbitrariness, but their success.
They hold not because they are exact, but because they survive approximation. They absorb error, tolerate deviation, and remain usable despite the fact that everyone involved understands their limits. In practice, enforcement relies less on the number itself than on judgments about reasonableness, risk, and context. The ‘fact’ persists because it is embedded in a network of practices, instruments, and shared expectations.
If you end up in court driving 60 in a 50, your ability to argue about instrument calibration won’t carry much weight. You’re already operating 20 per cent over specification. That’s beyond wiggle room – highly technical nomenclature, to be sure.
Blood alcohol limits work the same way. The legal threshold looks like a natural boundary. It isn’t. It’s a policy decision layered atop probabilistic measurement. Unemployment rates, diagnostic cutoffs, evidentiary standards – all of them look objective and immediate whilst concealing layers of judgment, calibration, and compromise. Each functions as a closure device: ending debate not because uncertainty has been eliminated, but because further uncertainty would make coordination impossible.
The trouble begins when we forget this – and we do. When facts are treated as simple givens rather than negotiated achievements, they become untouchable. Questioning them gets mistaken for denying reality. Acknowledging their construction gets misheard as relativism. What started as a practical tool hardens into something that feels absolute.
This is how we end up saying things like ‘just give me the facts’ whilst quietly relying on tolerance bands, interpretive discretion, and institutional judgment to make those facts usable at all.
If this sounds right – if facts work precisely because they’re mediated, not despite it – then the question becomes: what does truthfulness require once we’ve acknowledged this?
I’ve written a longer essay exploring that question, starting from Bernard Williams’ account of truthfulness as an ethical practice and extending it to facts themselves. The argument isn’t that facts are illusory or unreliable. It’s that recognising how they actually work – through stabilisation, constraint, and correction – clarifies rather than undermines objectivity.
The speed limit is the hint. Here’s the argument: The Fact of the Matter: After Bernard Williams – Truthfulness, Facts, and the Myth of Immediacy