We are governed by phantoms. Not the fun kind that rattle chains in castles, but Enlightenment rational ghosts – imaginary citizens who were supposed to be dispassionate, consistent, and perfectly informed. They never lived, but they still haunt our constitutions and television pundits. Every time some talking head declares “the people have spoken”, what they really mean is that the ghosts are back on stage.
👉 Full essay: Rational Ghosts: Why Enlightenment Democracy Was Built to Fail
The conceit was simple: build politics as if it were an engineering problem. Set the rules right, and stability follows. The trouble is that the material – actual people – wasn’t blueprint-friendly. Madison admitted faction was “sown in the nature of man”, Rousseau agonised over the “general will”, and Condorcet managed to trip over his own math. They saw the cracks even while laying the foundation. Then they shrugged and built anyway.
The rational ghosts were tidy. Real humans are not. Our brains run on shortcuts: motivated reasoning, availability cascades, confirmation bias, Dunning–Kruger. We don’t deliberate; we improvise excuses. Education doesn’t fix it – it just arms us with better rationalisations. Media doesn’t fix it either – it corrals our biases into profitable outrage. The Enlightenment drafted for angels; what it got was apes with smartphones.
Even if the ghosts had shown up, the math betrayed them. Arrow proved that no voting system can translate preferences without distortion. McKelvey showed that whoever controls the sequence of votes controls the outcome. The “will of the people” is less an oracle than a Ouija board, and you can always see whose hand is pushing the planchette.
Scale finishes the job. Dunbar gave us 150 people as the human limit of meaningful community. Beyond that, trust decays into myth. Benedict Anderson called nations “imagined communities”, but social media has shattered the illusion. The national conversation is now a million algorithmic Dunbars, each convinced they alone are the real people.
Why did democracy limp along for two centuries if it was this haunted? Because it was on life-support. Growth, war, and civic myth covered the cracks. External enemies, national rituals, and propaganda made dysfunction look like consensus. It wasn’t design; it was borrowed capital. That capital has run out.
Cue the panic. The defences roll in: Churchill said democracy was the “least bad” system (he didn’t, but whatever). Voters self-correct. Education will fix it. It’s only an American problem. And if you don’t like it, what – authoritarianism? These are less arguments than incantations, muttered to keep the ghosts from noticing the creaks in the floorboards.
The real task isn’t to chant louder. It’s to stop pretending ghosts exist. Try subsidiarity: smaller-scale politics humans can actually grasp. Try deliberation: citizens’ assemblies show ordinary people can think, when not reduced to a soundbite. Try sortition: if elections are distorted by design, maybe roll the dice instead. Try polycentric governance: let overlapping authorities handle mismatch instead of hammering “one will”. None of these are perfect. They’re just less haunted.
Enlightenment democracy was built to fail because it was built for rational ghosts. The ghosts never lived. The floorboards are creaking. The task is ours: build institutions for the living, before the house collapses under its own myths.
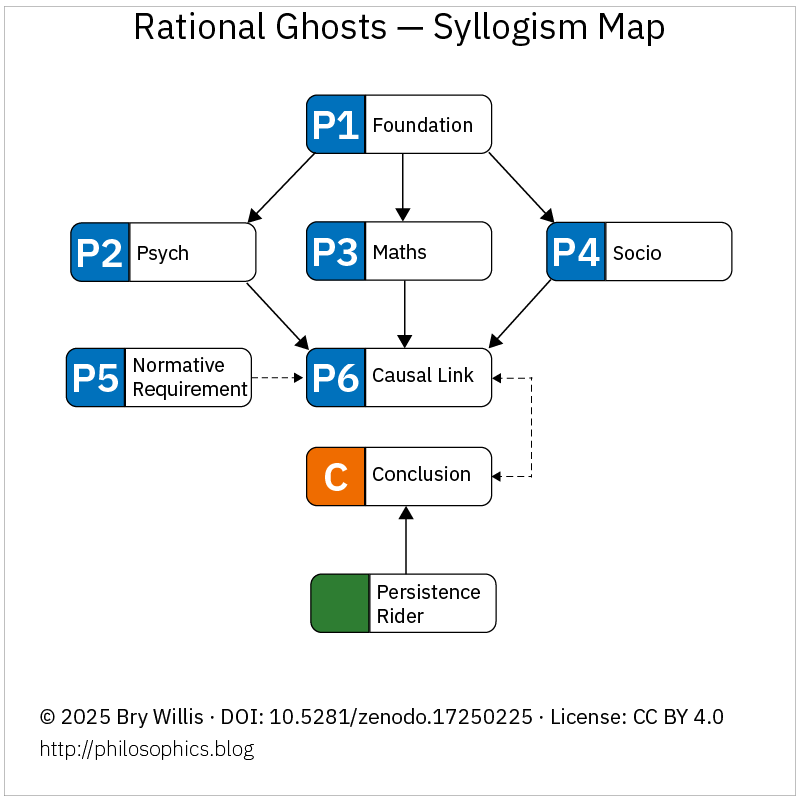
The Argument in Skeleton Form
Beneath the prose, the critique of Enlightenment democracy can be expressed as a syllogism:
a foundation that assumed rational citizens collides with psychological bias, mathematical impossibility, and sociological limits.
The outcome is a double failure – corrupted inputs and incoherent outputs – masked only by temporary props.