This is part 2 of a structural critique of Justice™. Read Part 1, The Ontology–Encounter–Evaluation Model: Retributive Justice as an Instantiation.
If you want a useful metaphor for how justice actually operates, don’t picture a blindfolded goddess with scales. Picture a casino.
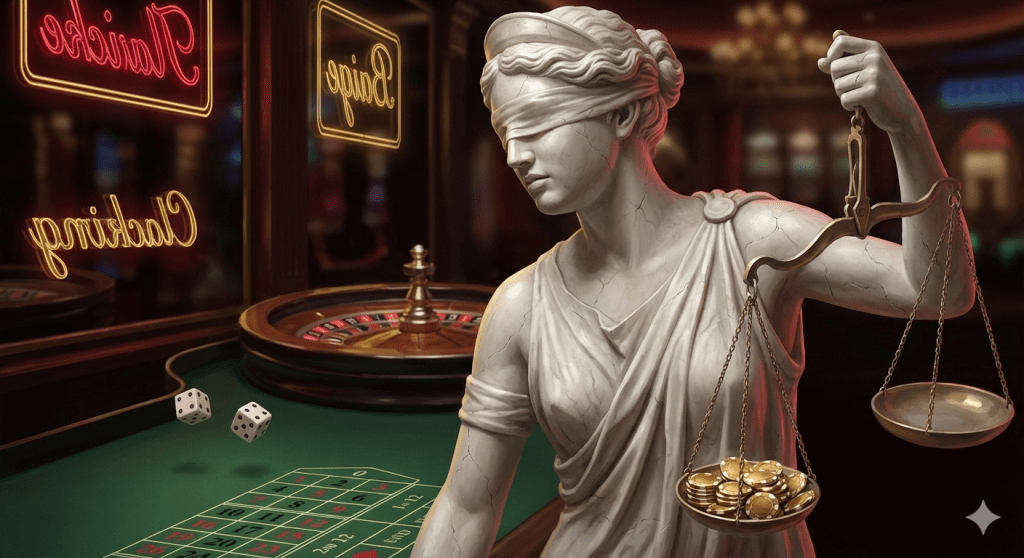

The rules are printed. The games look fair. Everyone is technically allowed to play. But the mathematics are tuned in advance, the exits are discreet, and the house never risks its own solvency. You don’t walk into a casino to discover whether chance is fair. You walk in to participate in a system whose advantage has already been engineered.
Justice works the same way
– like a casino with house-favoured odds.
By the time a defendant appears, the ontological dice have already been loaded. The system has quietly asserted a set of metaphysical commitments that make certain outcomes legible, actionable, and punishable – whilst rendering others incoherent, inadmissible, or ‘unreasonable’. Because I am a philosopher of language and not a lawyer, I am free from the indoctrination and selection bias inherent in that system. This allows me to critique the system directly without being excommunicated from the club.
What follows are not neutral assumptions. They are ontological wagers, each chosen because its alternative would tilt the field away from institutional power.
Ontology 1: The Self
Asserted (g): Diachronic, continuous self
Excluded (h): Episodic, fragmented, or non-self
Justice presumes that the person who acted yesterday is meaningfully the same entity standing in court today. This is not discovered; it is asserted.
Why? Because retribution requires persistence. Desert cannot attach to a momentary configuration of consciousness. Responsibility requires a carrier that survives time, memory gaps, psychological rupture, intoxication, trauma, and neurological variance.
An episodic self – Parfit’s reductionism, trauma-fractured identity, or situational selfhood – collapses the attribution pipeline. If the ‘self’ is a series of loosely connected episodes, punishment becomes conceptually incoherent. Who is being punished for whom?
So the law treats episodic accounts not as alternative ontologies but as defects: insanity, automatism, incompetence. The self is patched, not replaced.
The house needs continuity.
Without it, the game cannot settle accounts.
Ontology 2: Agency
Asserted (i): Robust individual agency
Excluded (j): Distributed, constrained, or illusory agency
Justice requires that actions originate somewhere. Agency is that somewhere.
The system asserts that agents could have done otherwise in a morally relevant sense. This is compatible with compatibilism, folk psychology, and everyday moral intuitions – but deeply hostile to hard determinism, strong situationism, or neurobiological deflation.
Why exclude weaker agency models? Because if agency dissolves into causation, environment, or neurochemistry, responsibility evaporates. At best, you get risk management. At worst, you get treatment or containment. Retribution has nowhere to land.
So the law nods politely to influences – upbringing, coercion, impairment – whilst ring-fencing agency as the default. Mitigation is permitted. Ontological revision is not. The house needs someone who could have chosen otherwise, even if that claim grows increasingly fictional under scrutiny.
The house needs someone who could have chosen otherwise
Ontology 3: Choice
Asserted (k): Discrete, identifiable choice points
Excluded (l): Continuous, coerced, or structurally constrained decision spaces
Justice models human action as a series of forks in the road. At some point, the agent ‘chose’ X over Y. This is enormously convenient.
Continuous decision spaces – poverty gradients, addiction loops, survival trade-offs – are messy. They resist clean counterfactuals. ‘What should they have done instead?’ becomes a sociological question, not a moral one.
So the system discretises. It locates a moment. A click. A trigger pull. A signature. A punch. A text sent.
Once the choice is frozen, the rest of the apparatus can proceed. Without discrete choice points, proportionality and culpability lose their anchor.
The house needs moments, not milieus.
Ontology 4: Causation
Asserted (m): Local, linear causation
Excluded (n): Diffuse, systemic, or emergent causation
Justice prefers causes that point: Who did this? When? How directly?
Systemic causation – economic pressure, cultural narratives, institutional design – creates attribution problems. If harm is emergent, no individual carries it cleanly. Responsibility smears.
So causation is narrowed. Chains are shortened. Proximate cause replaces contributing conditions. Structural violence becomes background noise.
This is not because systemic causation is false. It is because it is unmanageable within a retributive frame.
The house needs causes that fit inside a sentence.
Ontology 5: Reasonableness
Asserted (a): Normative moderation
Excluded (b): Atypical intensity, outsider rationalities
‘Reasonableness’ is the softest and most insidious ontology of the lot.
It pretends to be procedural, but it functions as cultural enforcement. The reasonable person is not an average human. They are an acculturated one.
Intensity becomes suspect. Rage becomes irrational. Grief becomes excessive. Radical interpretations become unreasonable not because they’re false, but because they disrupt cadence.
This ontology stabilises the game by disciplining tone. It doesn’t matter what you argue if you fail to argue it reasonably. Reasonableness is not required for responsibility to exist, only for dissent to be ignored.
Reasonableness is not required for responsibility to exist, only for dissent to be ignored.
The house needs calm players, not correct ones.
Why These Ontologies, and Not Their Rivals?
Because every excluded ontology threatens legibility. Justice is not designed to discover truth. It is designed to terminate cases. Ontologies that complicate attribution, disperse responsibility, or destabilise narrative continuity slow the machine. So they are ruled out – not explicitly, but structurally.
Once these commitments are in place, disagreement downstream becomes theatre. Arguments about fairness, proportionality, or intent occur within a rigged metaphysical envelope. That’s why reform debates feel sincere yet go nowhere. People argue outcomes whilst the house quietly keeps the rules.
The Point
None of this means justice is a scam. Casinos aren’t scams either. They do exactly what they are designed to do.
The problem is pretending the odds are neutral.
If you want to challenge justice meaningfully, you don’t start with sentencing guidelines or evidentiary thresholds. You start by asking which ontologies are being asserted – and why alternatives are unplayable.
Most people won’t make that move. Not because it’s wrong. Because it requires leaving the table.